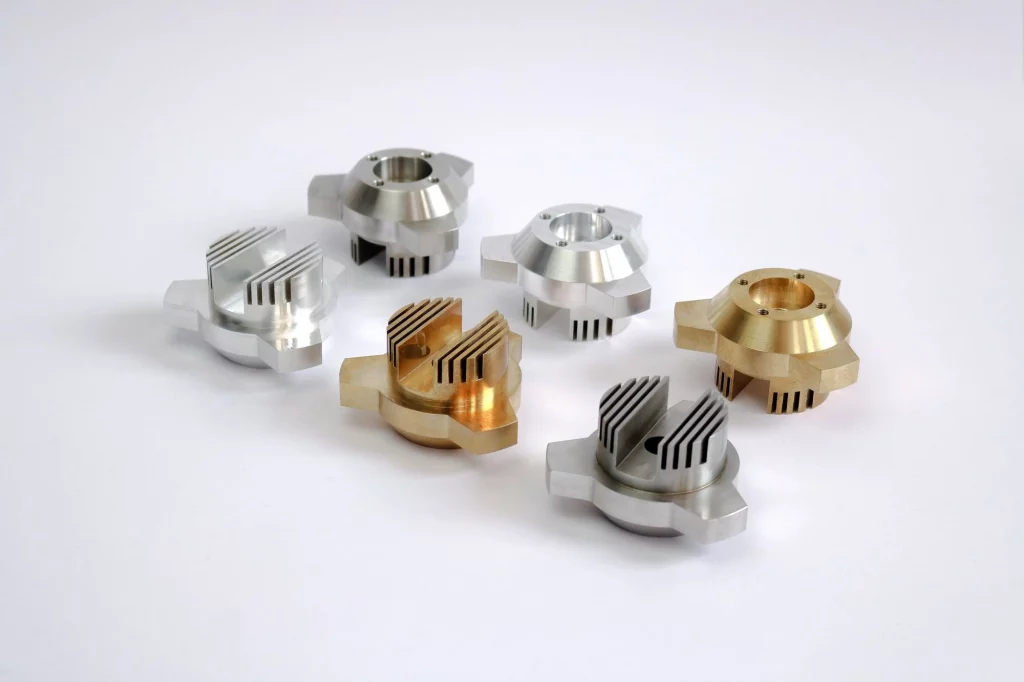

Are you struggling to quickly produce high-quality prototypes for your product development process? Rapid CNC prototyping is here to revolutionize your manufacturing experience.
With rapid CNC prototyping, you can effortlessly transform digital designs into physical models, parts, and components in record time. Say goodbye to the lengthy learning curve associated with traditional prototyping methods. This cutting-edge technology utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) machines to streamline the production process, saving you both time and costs.
Imagine having the power to create precise prototypes at a fraction of the usual time and expense. Rapid CNC prototyping allows you to bring your ideas to life swiftly and efficiently, enabling faster iterations and accelerated product development cycles.
So why wait? Dive into the world of rapid prototyping today and witness the transformative potential of this innovative technology!
Benefits of Rapid CNC Prototyping
Rapid CNC prototyping offers several advantages over traditional prototyping methods. With faster turnaround times, designers and engineers can iterate and test their designs more efficiently before moving into production. The precision and accuracy of CNC machining also ensure high-quality prototypes that closely resemble the final product.
Here are the key benefits of rapid CNC prototyping:
- Faster Turnaround Times: Compared to traditional prototyping methods, rapid CNC prototyping significantly reduces the time required to produce prototypes. This allows for quicker design iterations and faster product development cycles.
- Efficient Design Iteration: Rapid CNC prototyping enables designers and engineers to quickly create multiple iterations of their designs. They can easily make modifications, assess the results, and refine their concepts without lengthy delays.
- Enhanced Testing Capabilities: By producing functional prototypes using CNC machining, it becomes easier to conduct rigorous testing before committing to mass production. This helps identify any design flaws or performance issues early on, saving time and resources in the long run.
- Cost Savings: Rapid CNC prototyping eliminates the need for expensive tooling or molds typically associated with other manufacturing processes. It allows for cost-effective production of small quantities or custom parts without compromising on quality.
- Accurate Replication: The precision offered by CNC machining ensures that prototypes closely resemble the final product in terms of dimensions and surface finish. This level of accuracy is crucial for evaluating form, fit, and function during the prototype testing phase.
- Material Versatility: Rapid CNC prototyping supports a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, composites, and even exotic alloys. Designers have flexibility in choosing the most suitable material for their specific application requirements.
Applications of CNC Machined Prototypes
CNC machined prototypes find extensive applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, consumer electronics, and more. These prototypes serve multiple purposes such as functional testing, form verification, design validation, and market research.
The versatility of CNC machining enables the creation of complex geometries with intricate details that may not be achievable through other manufacturing processes. Engineers and designers can leverage CNC machining to produce prototype parts using lathes, machines, laser cutters, and other advanced equipment.
Key applications of CNC machined prototypes include:
- Functional Testing: CNC machined prototypes allow engineers to assess the functionality of a product before mass production. This helps identify any potential flaws or areas for improvement early on in the design process.
- Form Verification: By creating physical prototypes through CNC machining, designers can verify if the product’s form matches their initial concept accurately. This ensures that the final product meets aesthetic requirements.
- Design Validation: CNC machined prototypes offer a tangible representation of a design concept. Engineers can evaluate factors such as ergonomics, assembly feasibility, and overall performance to validate and refine their designs.
- Market Research Purposes: Companies often use CNC machined prototypes to gather feedback from potential customers during market research studies. These prototypes provide a realistic representation of the product’s appearance and functionality.
Understanding the CNC Prototype Machining Process
The CNC prototype machining process involves programming a computer-controlled machine to remove material from a solid block or sheet using cutting tools. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create a 3D model, which is then converted into machine-readable instructions (G-code). The machine precisely follows these instructions to shape the raw material into the desired prototype.
Here’s what you need to know about the CNC prototype machining process:
- CAD Design: Start by creating a 3D model of your prototype using CAD software. This software allows you to design and visualize your product before manufacturing.
- G-Code Conversion: Once the design is complete, it needs to be converted into machine-readable instructions called G-code. This code tells the CNC machine how to move and cut the material accurately.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material for your prototype based on its intended use and requirements. Common materials include metals like aluminum or stainless steel, as well as plastics such as ABS or nylon.
- Machining Setup: Prepare the CNC machine for prototyping by securing the chosen material firmly in place. This ensures stability during the cutting process and prevents any unwanted movement that could affect precision.
- Tool Selection: Select suitable cutting tools for different aspects of your design, such as milling cutters or drills for specific features or details required in your prototype.
- Precision Machining: The CNC machine will follow the programmed G-code instructions precisely, removing excess material and shaping it according to your design specifications.
- Quality Control: Regularly inspect and measure the prototype during machining to ensure accuracy and adherence to tolerances specified in your design.
- Finishing Touches: After completion of rough machining, additional processes like sanding, polishing, or painting may be required depending on your desired finish and presentation.
By understanding this rapid CNC prototyping process and its various steps, you can efficiently bring your ideas to life and create functional prototypes for testing or showcasing your product.
Precision, Quality, and Affordability: Achieving Excellence at Any Volume
With rapid CNC prototyping, precision is achieved through the use of advanced computer-controlled machines that consistently produce accurate results. These machines are capable of working with a variety of materials, allowing for precise manufacturing of intricate designs. The industry-leading tolerances offered by CNC machining ensure that every product meets the desired specifications.
The quality of CNC machined prototypes surpasses many other prototyping methods due to their high level of detail and surface finish capabilities. CNC machines have the power to create complex geometries with exceptional accuracy and depth, resulting in a finished product that closely matches the intended design. The laser-like precision enables manufacturers to produce prototypes with consistent thickness and tolerance throughout the production process.
Despite its initial setup costs, rapid CNC prototyping becomes cost-effective for larger volumes, as the per-unit cost decreases significantly. This makes it an ideal choice for both small-scale projects and mass production needs. By leveraging the capabilities of CNC machining services, businesses can save on transportation expenses and reduce lead times while maintaining superior quality standards.
Request a Quote for Your CNC Prototyping Project
Now that you’ve learned about the benefits and applications of rapid CNC prototyping, as well as gained an understanding of the machining process and the importance of precision and quality, it’s time to take the next step. If you have a project in mind or need parts manufactured quickly, don’t hesitate to request a quote for your CNC prototyping needs. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in bringing your ideas to life with speed and accuracy. Whether you’re a small business owner looking to test a new product or an engineer seeking high-quality prototypes, we’ve got you covered.
So why wait? Contact us today and let’s get started on your CNC prototyping project. With our state-of-the-art technology, experienced professionals, and commitment to excellence, we guarantee that you’ll be satisfied with the results. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to bring your designs from concept to reality efficiently and affordably. Request a quote now and experience the advantages of rapid CNC prototyping firsthand.
FAQs
How long does it typically take for CNC prototypes to be manufactured?
The manufacturing time for CNC prototypes can vary depending on factors such as complexity, quantity, and material selection. However, in most cases, rapid CNC prototyping allows for significantly shorter lead times compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It is best to consult with our team directly regarding your specific project requirements.
What materials can be used for CNC prototyping?
CNC prototyping offers versatility. Commonly used materials include metals like aluminum and steel, as well as plastics such as ABS and nylon. The choice of material depends on factors like desired strength, appearance, functionality, and budget constraints.
Can I make design changes during the CNC prototyping process?
Yes! One of the advantages of rapid CNC prototyping is its flexibility in accommodating design iterations. With the ability to quickly modify digital designs and produce updated prototypes, you can refine your product’s features and specifications as needed.
Are CNC prototypes suitable for functional testing?
Absolutely! CNC prototypes are widely used for functional testing purposes. The high precision and accuracy of CNC machining ensure that the prototypes closely resemble the final product, allowing engineers and designers to evaluate its performance, fit, and functionality.
What file formats are compatible with CNC prototyping?
Most CNC machines accept common CAD file formats such as .STL, .STEP, .IGES, and .DWG. However, it is recommended to check with our team regarding specific file format requirements for your project. We will work closely with you to ensure a seamless transition from your digital design to a physical prototype.


 Español
Español